For pediatric patients with moderate to severe Crohn’s disease (CD)
Remission and response for pediatric patients with CD1
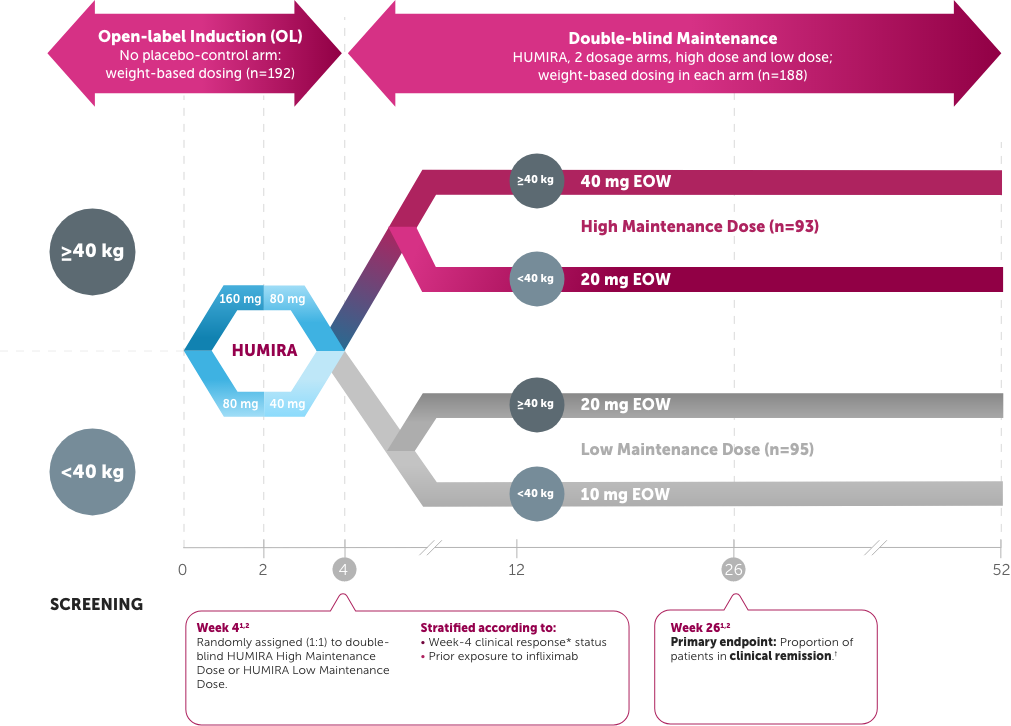
IMAgINE
Pediatric patients with moderate to severe CD (PCDAI score >30) who had, over the previous 2-year period, an inadequate response to or intolerance to corticosteroids or an immunomodulator1,2
Study Design Intro: A multicenter, 4-week, open-label induction followed by 52-week, double-blind, randomized, maintenance study of 2 dose levels of HUMIRA in moderate to severe pediatric CD in patients (PCDAI score >30) who had, over the previous 2-year period, an inadequate response to or intolerance to corticosteroids or an immunomodulator. Patients who previously had loss of response to or intolerance to infliximab were allowed entry to trial. Clinical remission and response rates were numerically higher in the High Maintenance Dose group compared with the Low Maintenance Dose group, and those differences were either not statistically significant or exploratory.1,2
The endpoint was a comparison of the High Maintenance Dose vs. the Low Maintenance Dose. Only the High Maintenance Dose results are depicted.1,2
Remission: Weeks 26 and 521,2,*
Patients were 55% bio-naïve and 45% bio-experienced
Dosing based on Week 4 weight (<40 kg=20 mg, ≥40 kg=40 mg); every other week (EOW)

DATA LIMITATIONS
Clinical remission at Week 4 was an exploratory endpoint and was not powered or tested to demonstrate a statistically significant difference in treatment effect; no statistical inferences can be made due to the exploratory nature of the analysis.
Adverse events in IMAgINE 1 study population (n=192)1
- 67% of children experienced an infection, including upper respiratory tract infection and nasopharyngitis.
- 5% of children experienced a serious infection (these included viral infection, device-related sepsis [catheter], gastroenteritis, H1N1 influenza, and disseminated histoplasmosis).
- Allergic reactions were observed in 5% of patients. All of them were non-serious and primarily localized reactions.
*Clinical remission was defined as PCDAI score of ≤10.
PCDAI=Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; TNF=tumor necrosis factor
Response: Weeks 26 and 521,2,*
Patients were 55% bio-naïve and 45% bio-experienced
Dosing based on Week 4 weight (<40 kg=20 mg, ≥40 kg=40 mg); every other week (EOW)

*Clinical response was defined as a decrease in PCDAI score of ≥15 points from baseline.
PCDAI=Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Activity Index
Remission rates: bio-naïve and bio-experienced pediatric CD patients (Week 4 post-hoc and Weeks 26 and 52 subgroup analyses)1-3,*,†
- Total population
- Bio-naïve
- Bio-experienced
- Total population
- Bio-naïve
- Bio-experienced
- Total population
- Bio-naïve
- Bio-experienced
DATA LIMITATIONS
These data were not powered or tested to demonstrate a statistically significant difference in treatment effect; no statistical inferences can be made due to the exploratory nature of the analyses.
*Clinical remission was defined as Pediatric Crohn's Disease Activity Index (PCDAI) score of ≤10.
†Bio‑naïve and bio‑experienced refers to patients that were infliximab‑naïve and infliximab‑experienced.
Response rates: bio‑naïve and bio‑experienced subgroup at Weeks 26 and 52 (subgroup analyses)1,2,*,†
- Total population
- Bio-naïve
- Bio-experienced
- Total population
- Bio-naïve
- Bio-experienced
DATA LIMITATIONS
These data were not powered or tested to demonstrate a statistically significant difference in treatment effect; no statistical inferences can be made due to the exploratory nature of the analyses.
The endpoint was a comparison of the High Maintenance Dose vs. the Low Maintenance Dose. Only the High Maintenance Dose results are depicted.2
*Clinical response was defined as a decrease in PCDAI score of ≥15 points from baseline.
†Bio-naïve and bio-experienced refers to patients that were infliximab-naïve and infliximab-experienced.
Safety data: treatment-emergent adverse events (AEs) through 52 Weeks2,*
High Maintenance Dosea: 40 mg/20 mg EOW
| Adverse Event | N=93, % (n) | PYs=54.1, Events (E/100 PYs) |
| Any AE | 92.5% (86) | 507 (937.2) |
| Severe AE | 20.4% (19) | 27 (49.9) |
| Serious AEb | 23.7% (22) | 24 (44.4) |
| Leading to discontinuation of study drug | 16.1% (15) | 20 (37.0) |
| Infectious AE | 60.2% (56) | 98 (181.1) |
| Serious infectionsc | 5.4% (5) | 5 (9.2) |
| Opportunistic infections, excluding TB | 1.1% (1) | 1 (1.8) |
| Any malignancies | 0 | 0 |
| Injection site reactions | 9.7% (9) | 25 (46.2) |
| Hepatic-related AE | 4.3% (4) | 5 (9.2) |
| Allergic reactions | 6.5% (6) | 8 (14.8) |
| Hematologic-related AE | 9.7% (9) | 11 (20.3) |
aPatients may have received concomitant conventional therapies.
bSerious AEs were defined as fatal or immediately life-threatening; required inpatient hospitalization or prolonged existing hospitalization; resulted in persistent or significant disability/incapacity; congenital anomaly; spontaneous or elective abortion; or required medical or surgical intervention to prevent a serious outcome.
cAbdominal abscess, histoplasmosis disseminated, gastroenteritis, anal abscess, H1N1 influenza.
*Treatment-emergent AEs were any AEs with an onset date on or after the first double-blind dose and up to 70 days after the last dose of study drug or up to the first dose of weekly blinded adalimumab.